Ultra-strength combined with extreme temperature capabilities
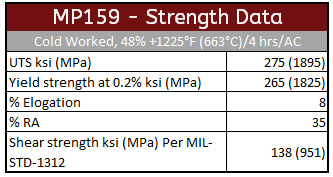
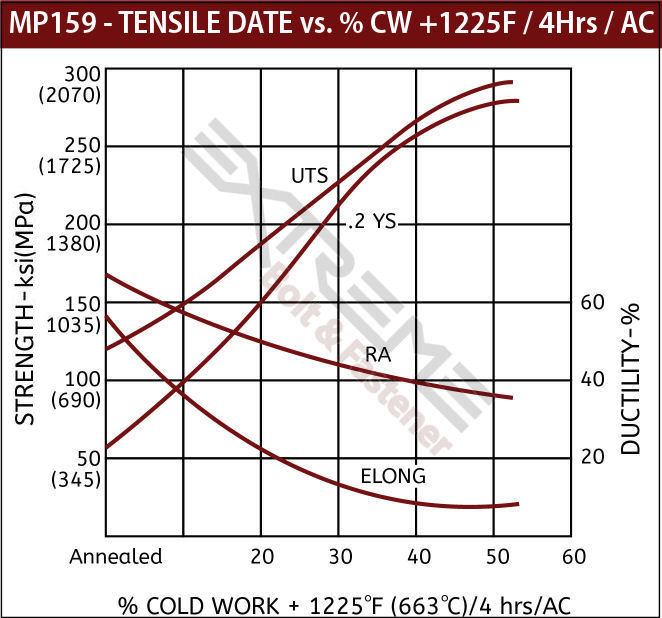
- Extreme high strength properties up to 275 ksi ultimate tensile.

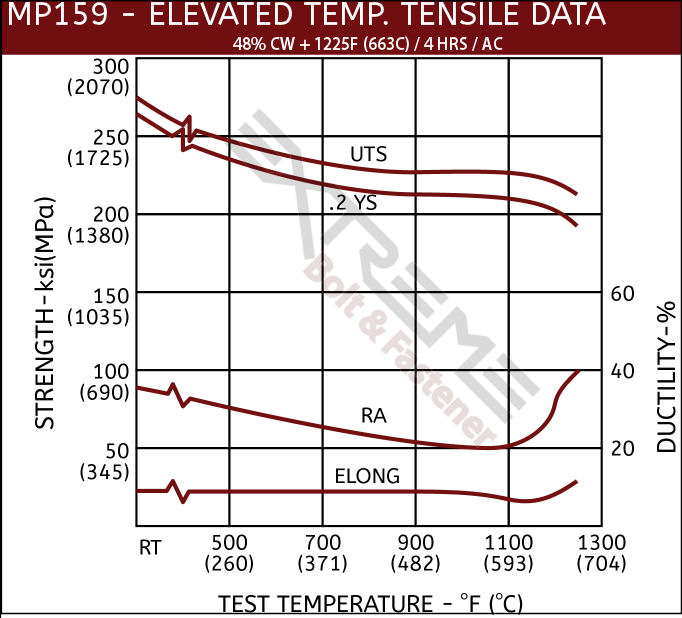
- Maintains superior strength to 1100°F.
- MP159 chemisty and specification
- Datasheet for MP159
As aerospace engineering advances, so must the materials to meet the technological requirements of this industry. Threaded rods made from MP159 have been developed to provide a solution to high temperature, high strength components. MP159 threaded rods offer strength capabilities similar to other Cobalt Alloys (MP35N) but can be used at much higher temperatures - up to 1100°F, compared to MP35N’s usable limit of 800F. In addition, MP159 threaded rods can be used beyond 1100°F in short term situations.
Key Benefits
- High ultimate tensile strength of 275 ksi and yield strength of 265 ksi (Cold Worked and Age Hardened) combined with excellent ductility and toughness
- Similar corrosion resistance compared to MP35N which is usable in mineral acids, hydrogen sulfide, seawater and salt spray environments.
- Excellent fatigue resistance and creep strength at elevated temperatures
- Excellent resistance to crevice corrosion, stress corrosion cracking and hydrogen embrittlement
Applications
- The aerospace industry relies on MP159 threaded rods for its most advanced gas turbine and jet engines, rocket boosters and jet propulsion systems.
- Power generation and chemical processing utilize MP159 threaded rods for applications that demand high strength at extreme temperatures.
Resources: MP159 Torque Spec
MP159 Fastener Types: Bolts, Nuts, Screws, Studs, Threaded Rod, Washers
MP159 Chemistry and Specifications
MP159N Specifications: UNS R30159

MP159 High Strength Data