From sea water to strong acids
From sea water to strong acids
Corrosion is one of the most common causes of fastener failure. From salt water applications to hot concentrated acids, Extreme Bolt & Fastener offers the most corrosion resistant fasteners to protect against even the harshest applications. Below are guides showing the performance of a variety of corrosion resistant fasteners in various corrosive media, as well as a general comparison of specialty metal and engineered polymer fasteners. We also have resources to better help your understanding of the types of corrosion you may face, such as pitting, crevice and galvanic corrosion. In-depth, information can also be found on the material specific sections of this site. For additional assistance, contact our experienced engineering staff to help guide you to the best material.
- Hydrobromic Acid (HBr)
- Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
- Hydrofluoric Acid (HF)
- Nitric Acid (HNO3)
- Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4)
- Salt water / Sea water
- Sour Gas (Hydrogen Sulfide/H2S)
- Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4)
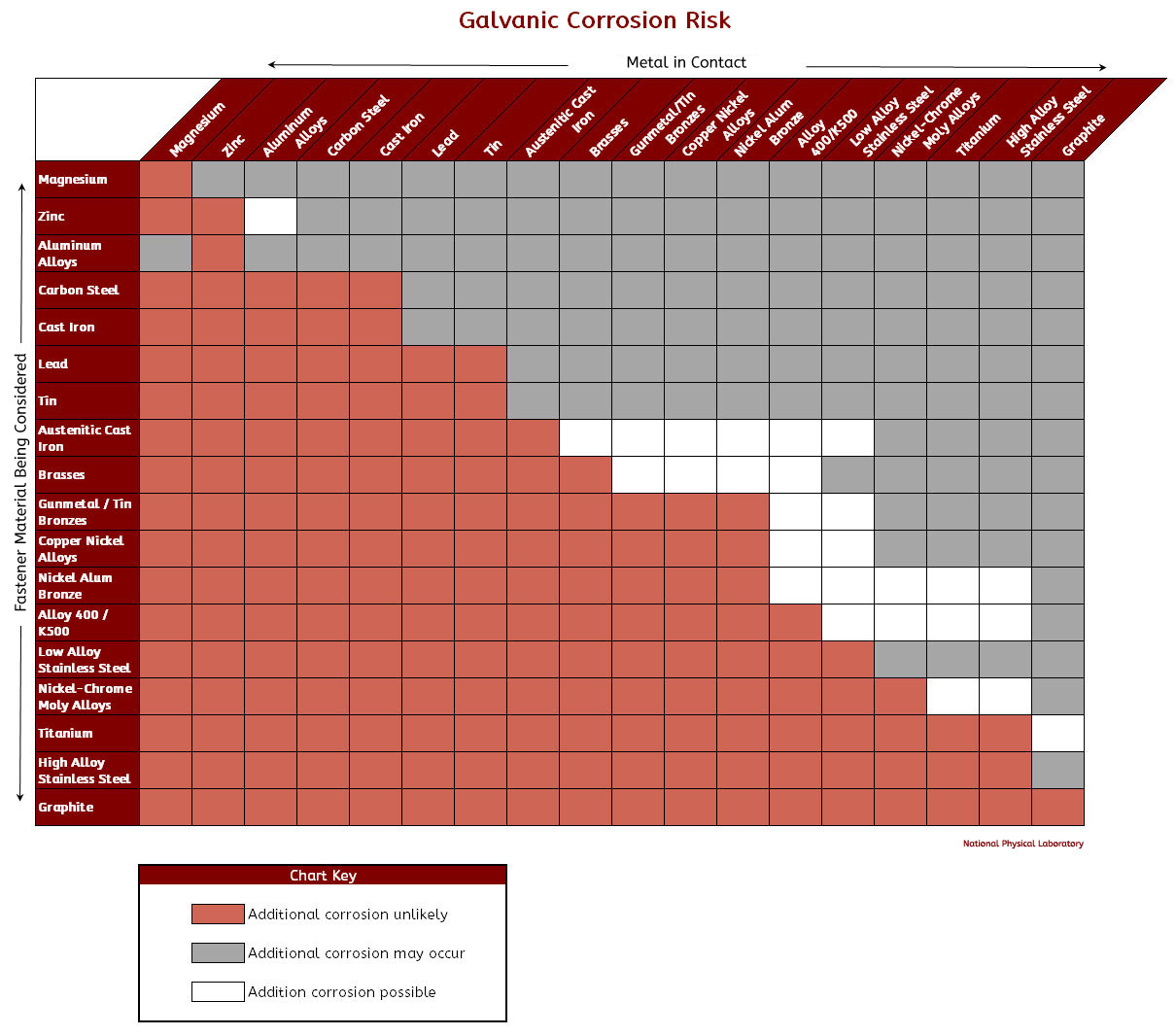
Resources: Types of Fastener Corrosion, Galvanic Corrosion Chart, Understanding Nickel Alloy Fasteners
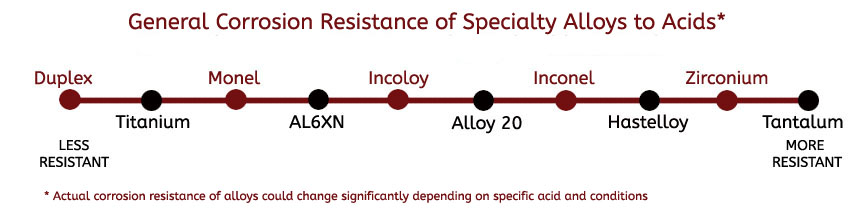
Specialty metal fasteners provide corrosion solutions to even the harshest chemical environments, as well as marine and salt water applications. Though their performance varies greatly by material and corrosive environment, the chart below will give you a general guide on the most verses least resistant materials (though actual corrosion resistance could be very different based on the exact environment). Nickel alloys are some of the most commonly used metals for corrosion, but titanium, zirconium and tantalum also play an enormous role in extreme corrosion. For more in-depth information, visit our material specific pages or contact one of our engineers.
- Overview of the most common nickel alloys
- Nickel alloy corrosion comparison
- Hastelloy, zirconium and tantalum hydrochloric acid corrosion comparison
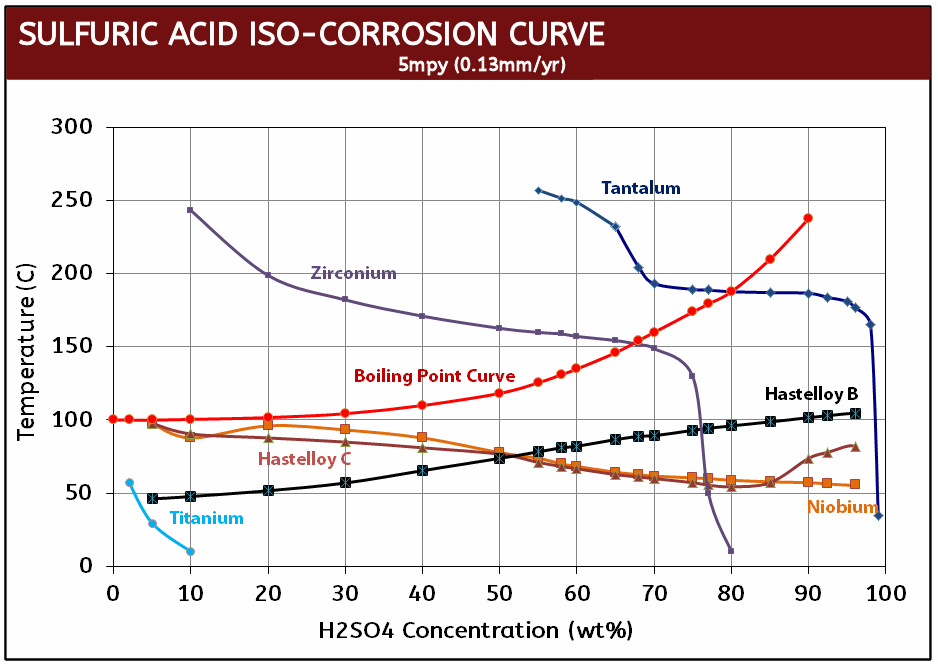
- Hastelloy, zirconium and tantalum corrosion sulfuric acid comparison
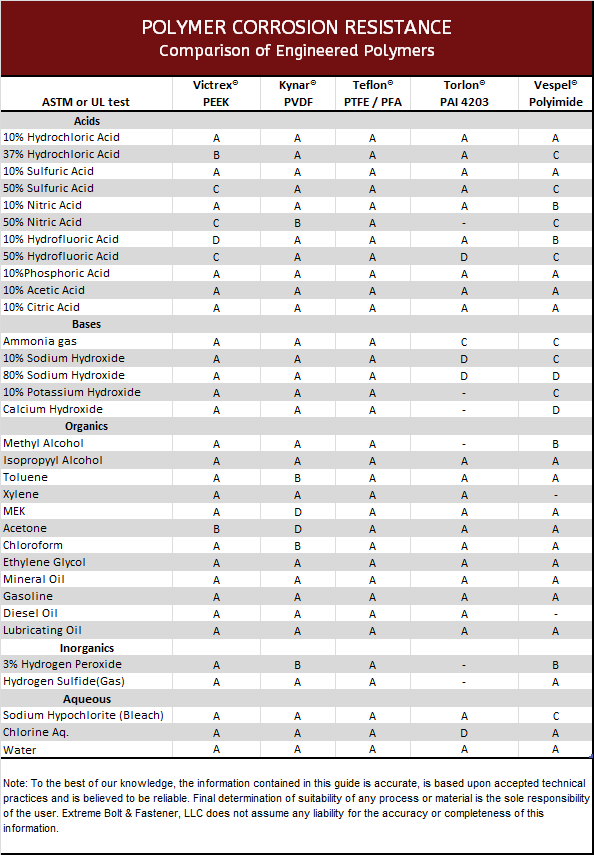
Though polymer fasteners can’t handle the high temperatures of metals, they do have the ability to provide excellent corrosion resistance acidic conditions. This chart gives you a basic perspective of their corrosion capabilities. For more information on each polymer, visit our material specific pages or contact one of our engineers.

- Comparison of corrosion resistant polymers
- PTFE
- PFA
- PVDF/Kynar
- Vespel
- Torlon
- PEEK
Comparison of Corrosion Resistant Polymers
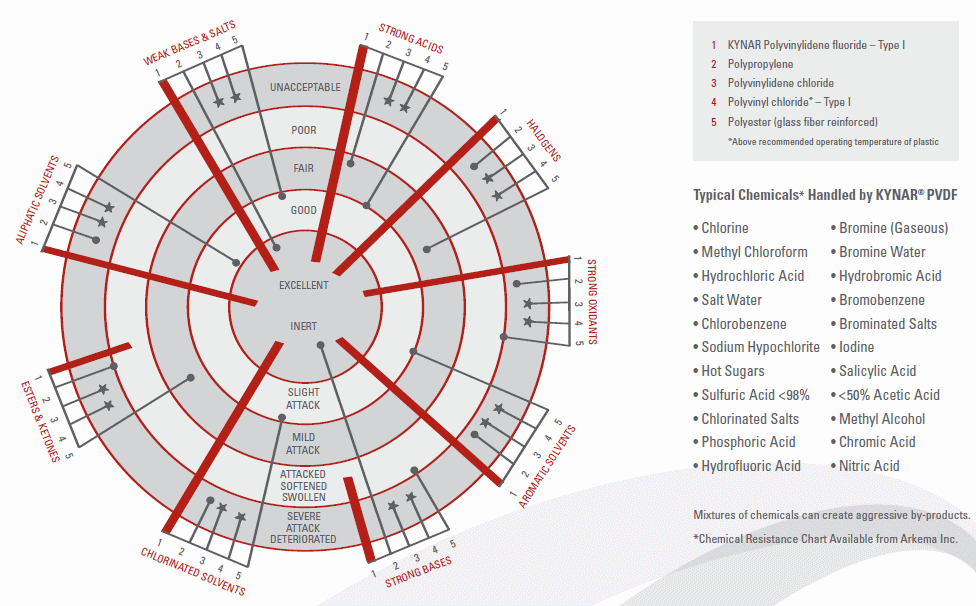
Corrosion Resistance of PVDF / Kynar
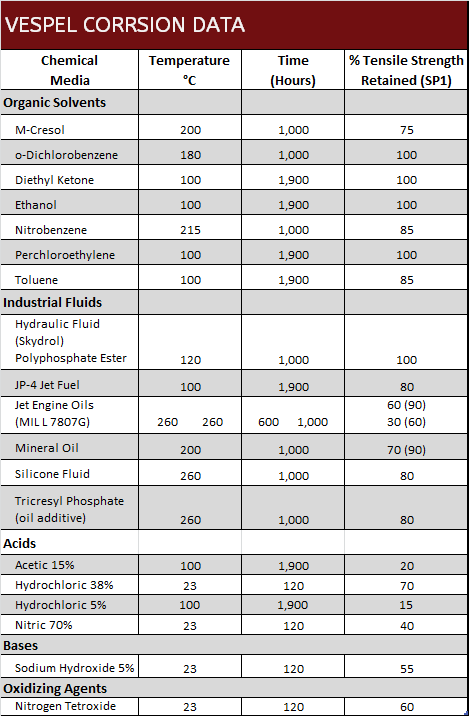
Vespel Corrosion / Chemical Resistance Data
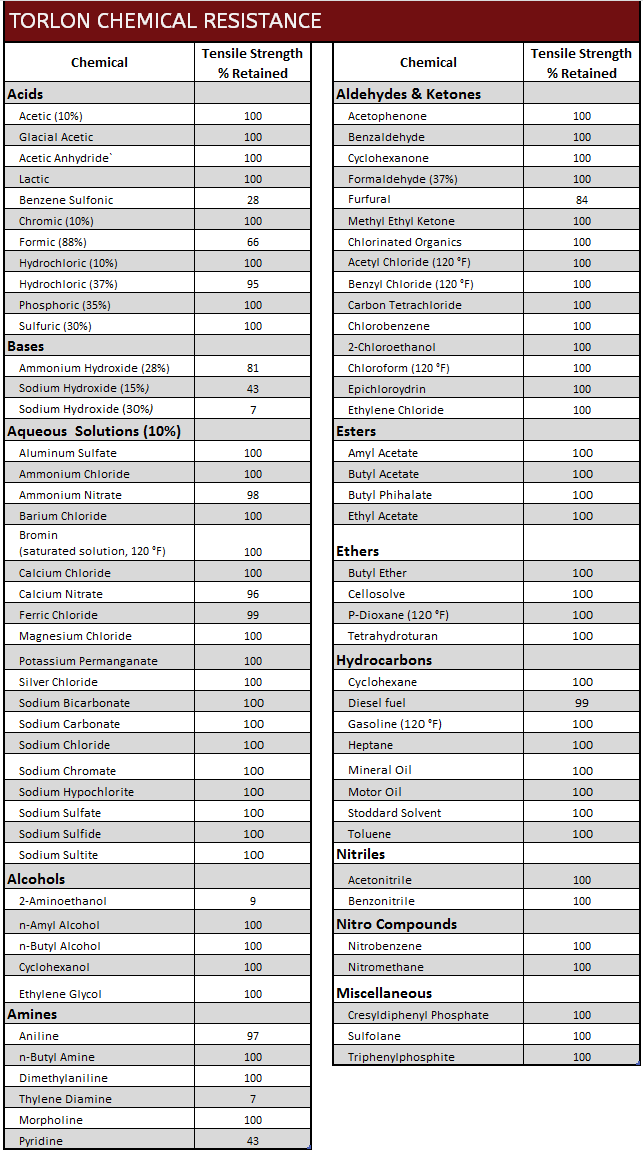
Torlon Corrosion / Chemical Resistance Data
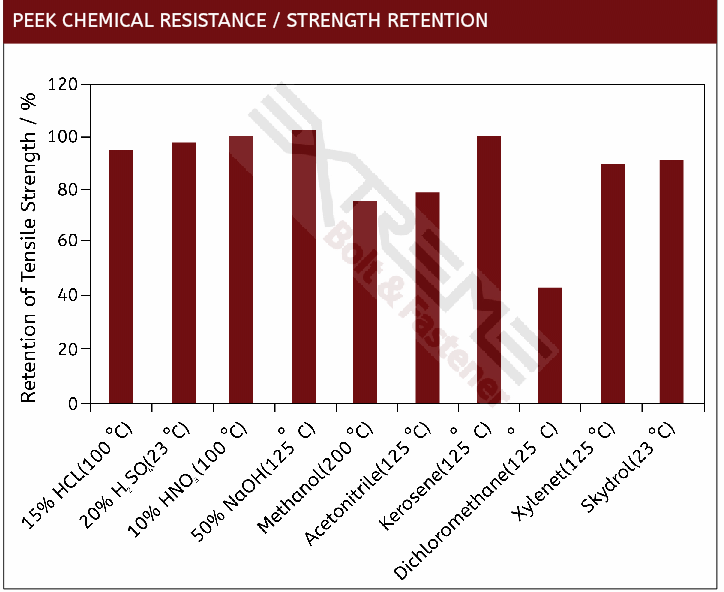
PEEK Corrosion / Chemical Resistance
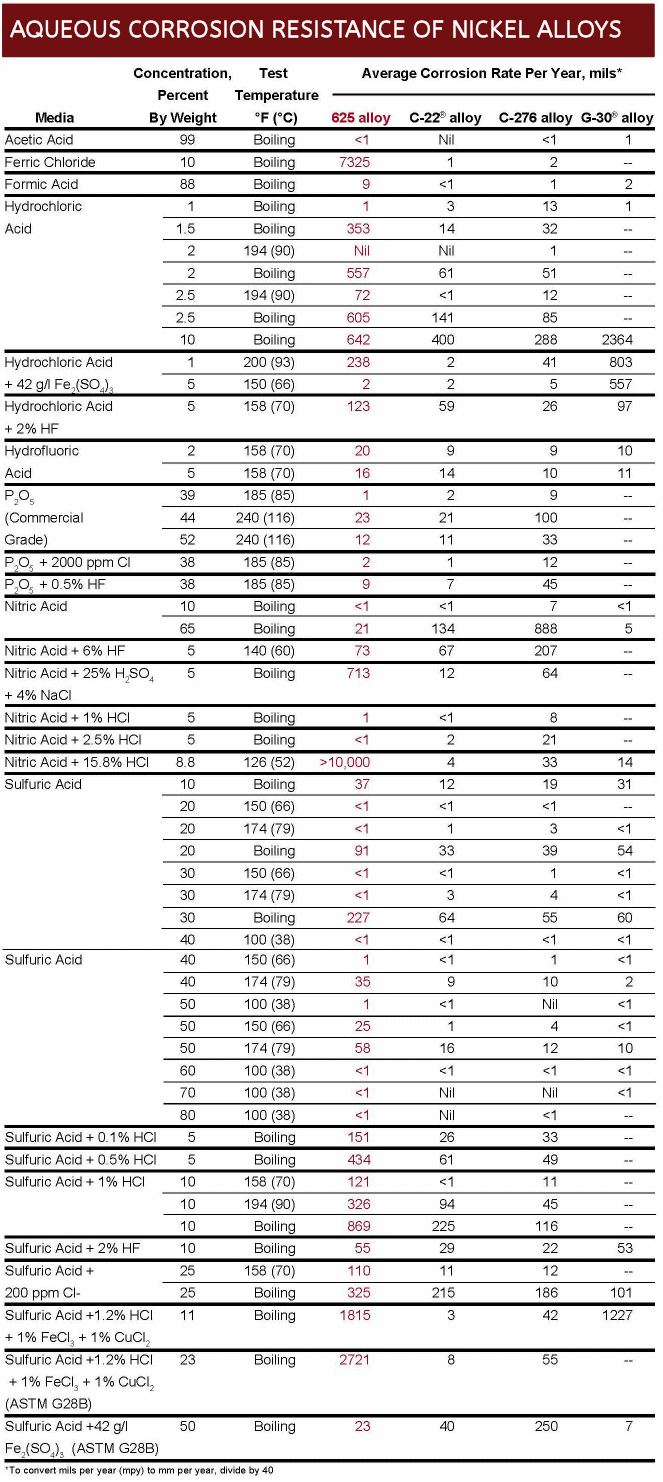
Corrosion Resistance Comparison of High Performance Nickel Alloys
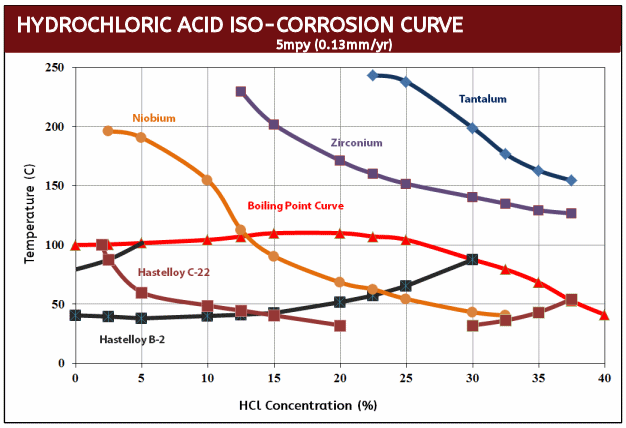
Tantalum, Zirconium & Hastelloy / HCl Iso-Corrosion Curves
Tantalum, Zirconium & Hastelloy / H2SO4 Iso-Corrosion Curves