A Ni-Cr alloy known for its corrosion resistance and high temperature stability
- Good corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures

- High temperature stability up to 2200°F (982°C)
- High strength material with excellent toughness at elevated temperatures
- Available in: Inconel 600 and Inconel 625
- Inconel weld stud features and benefits
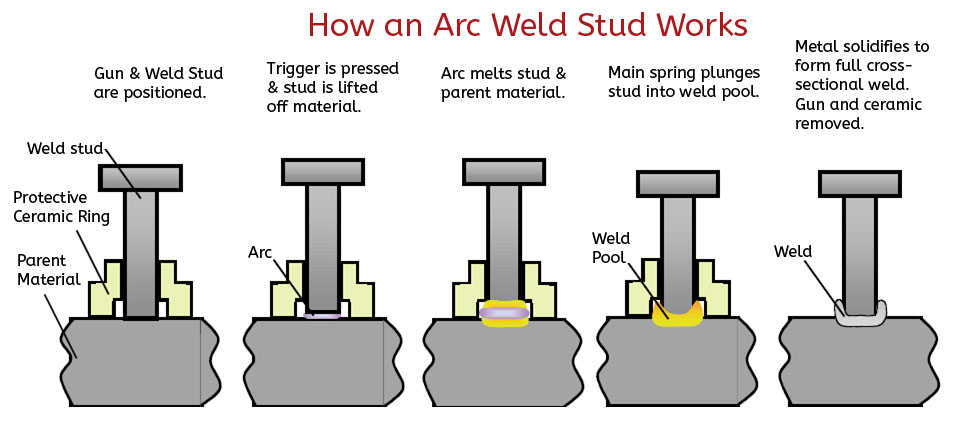
- How an Inconel arc weld stud works
- Datasheets available on Inconel 625 and Inconel 718
Inconel weld studs are available in a variety of fastener styles for manual (MIG, TIG) arc and capacitor discharge welding methods. Combined with the high-temperature, corrosion resistant strength of Inconel 625 and 600, these weld studs provide a secure, cross-sectional weld in single-sided access situations for a wide variety of extreme environments. In mild environments, such as the atmosphere, sea water, neutral salts, and alkaline media, there is almost no attack to Inconel weld studs. In more severe corrosive environments the combination of nickel and chromium provides Inconel weld studs resistance to oxidizing chemicals, whereas the high nickel and molybdenum contents supply resistance to non-oxidizing environments.
Because Inconel 600 and Inconel 625 weld studs offer a good balance of corrosion resistance, temperature stability, toughness and strength they are often a material of choice for chemical processing, aerospace, marine, electronics and oil & gas.
The most commonly used grades of Inconel nickel alloy fasteners are Inconel 625 and Inconel 718. Gain more insight on these two grades by accessing our Inconel 625 and Inconel 718 overviews or by contacting our engineering experts.
Resources: Inconel Torque Spec, Inconel 625 screws, Inconel 718 screws
Screw Types: 12 Point Screws, Button Head Cap Screws, Flat Head Screws, Hex Cap Screw, Pan Head Screws, Set Screws, Socket Head Cap Screws, Torx Screws, Vented Screws
Inconel Weld Stud Features & Benefits
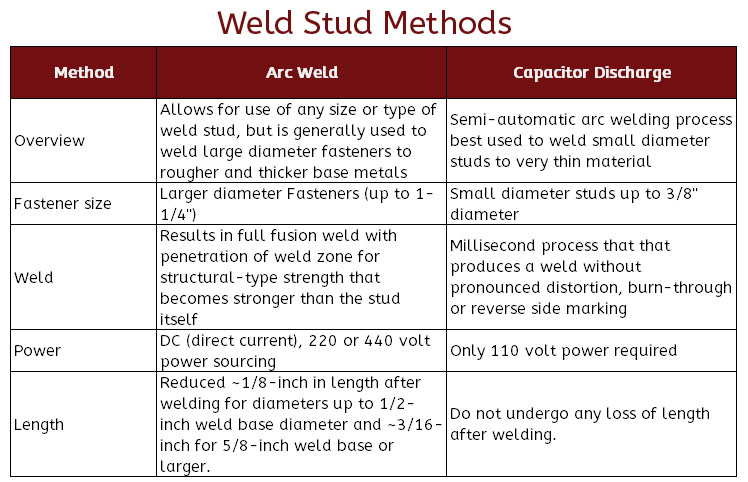
Inconel weld studs are an ideal way to securely attached fasteners in extreme applications where reaching both sides of a structure is impossible or undesired. These weld studs can be attached by a variety of welding techniques, such as MIG or TIG welding or they can be attached by automated welding guns using Arc or Capacitor Discharge (CD) technologies.
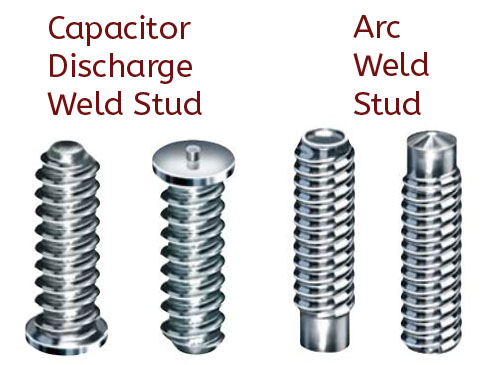 Arc and Capacitive Discharge (CD) Weld Stud Benefits
Arc and Capacitive Discharge (CD) Weld Stud Benefits
- Security: Unlike the peripheral weld used on a common bolt, the weld used to secure a weld stud fastener is a full cross sectional weld, so the full face of the fastener is welded in place for a strong, secure hold. And since there are no drilled holes – which weakens the structural integrity of the application – the attachment is even stronger.
- Speed: Installing an Inconel weld stud is a fast and simple process with a most fasteners taking less than 1 second to weld in place. Plus there is no secondary work such as drilling, polishing or grinding.
- Simplicity: Weld studs require almost no special skills and minimal training and equipment is needed for installation. In addition, the equipment is also portable.
- Variety: Inconel weld studs are available in a wide variety of fastener styles including (but not limited to) fully threaded, partially threaded, full base, reduced base, long, tapped base, and shoulder thread to name a few.
Common Inconel Weld Stud Grades, Chemistry & Specifications
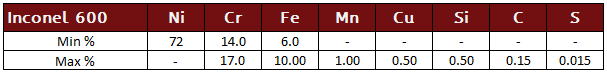
Inconel 600
Alloy 600, UNS N06600, is a nickel-chromium alloy with good carburization and oxidation resistance through 2000°F. The alloy has long been used in the heat treating industry and Inconel 600 has useful resistance to dry Cl2 and HCl gases at moderately elevated temperatures.
Inconel 600 Specifications: AMS 5540, AMS 5665, ASME SB 166, ASME SB 167, ASME SB 168, ASTM B 166, ASTM B 167, ASTM B 168, EN 2.4816, UNS N06600, Werkstoff 2.4816
Inconel 625
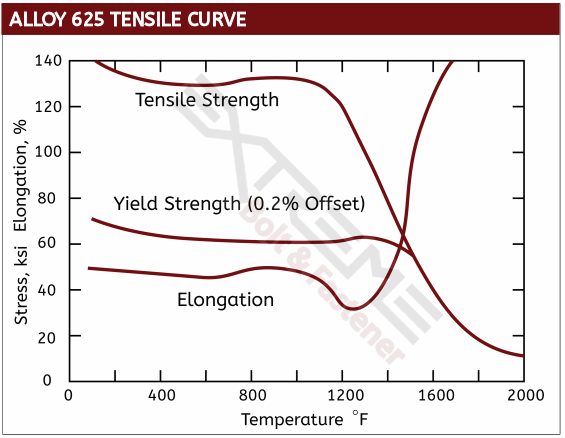
Inconel 625, UNS N06625, is the workhorse of the Inconel family and is one of the most common grades. It exhibits high creep-rupture strength and is oxidation resistant to 1800°F (982°C). Inconel 625 has excellent resistance to hot seawater, scrubber environments and reducing acids and this alloy resists a wide range of severely corrosive environments and is especially resistant to pitting and crevice corrosion.
Inconel 625 Specifications: AMS 5666, AMS 5837, ASME SB 443 Gr 1, ASME SB 446 Gr 1, ASTM B 443 Gr 1, ASTM B 446 Gr 1, EN 2.4856, ISO 15156-3, NACE MR0175-3, UNS N06625, Werkstoff 2.4856

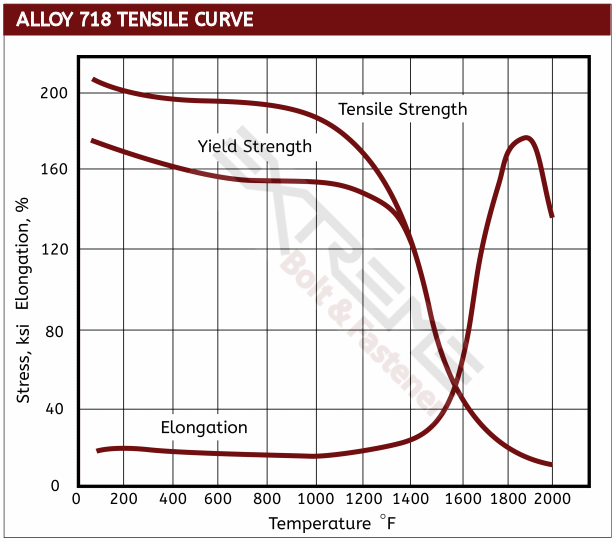
Mechanical Data
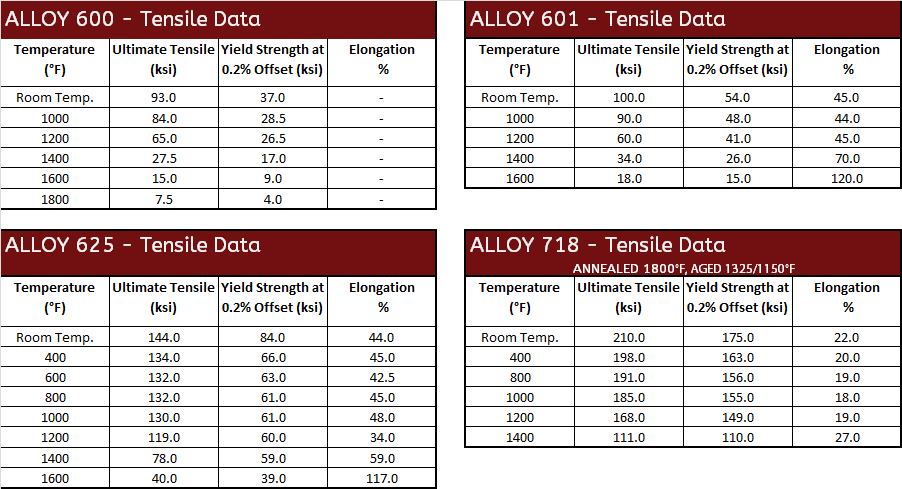
 |  |
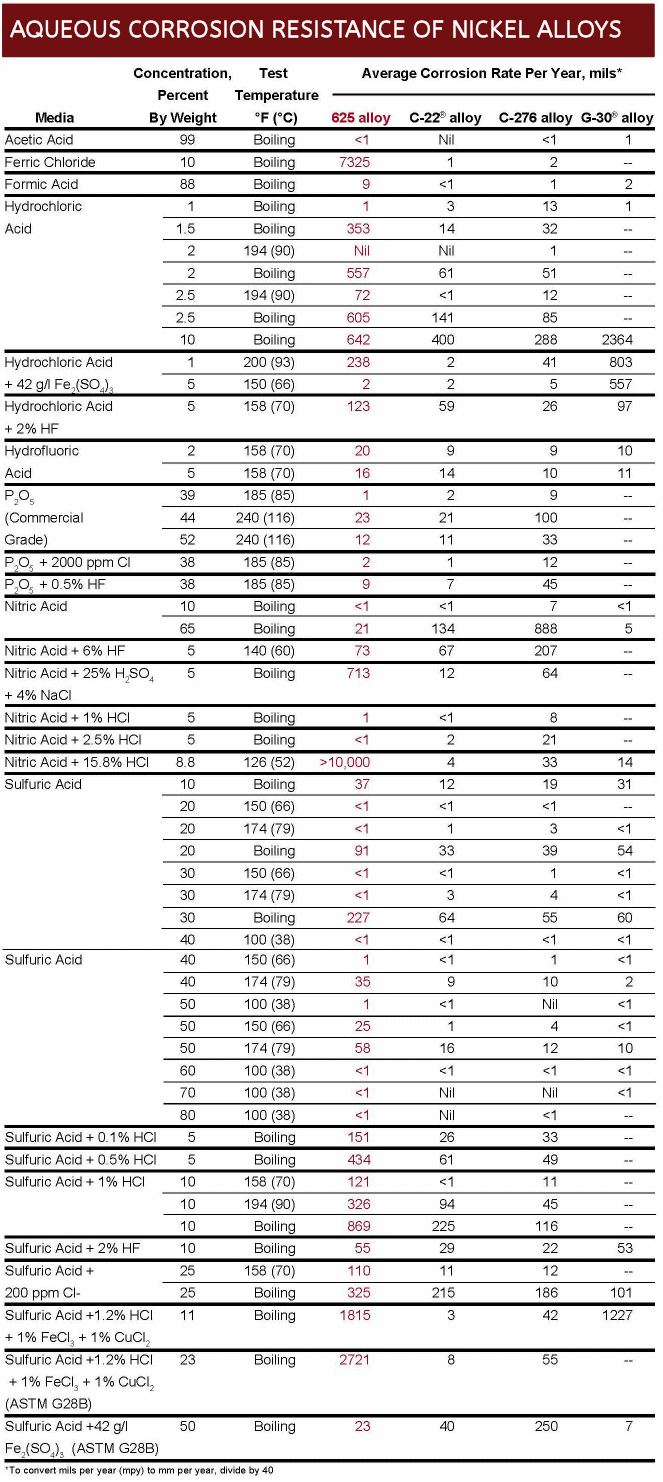
Inconel Corrosion Data