A Ni-Cu alloy with high strength and good corrosion resistance
- Excellent resistance to hydrofluoric acid
- Excellent resistance to sea water for marine applications
- Useful in cryogenic applications
- High strength metal with good toughness at high temperatures
- Monel Grades: Alloy 400 and K500
- In-depth information on grades 400 and K500
- Datasheets available for Monel 400 and Monel K500
Strength & Saltwater Resistance
Monel® socket head cap screws are made from a nickel-copper alloy that exhibits high strength, toughness and good corrosion resistance. Renowned for the saltwater corrosion resistance, Monel is the go-to material by the navy. It is often used in many other marine applications for its combination of high strength and seawater resistance. Monel screws are even resistant to rapid moving seawater and will last many years in saltwater conditions.
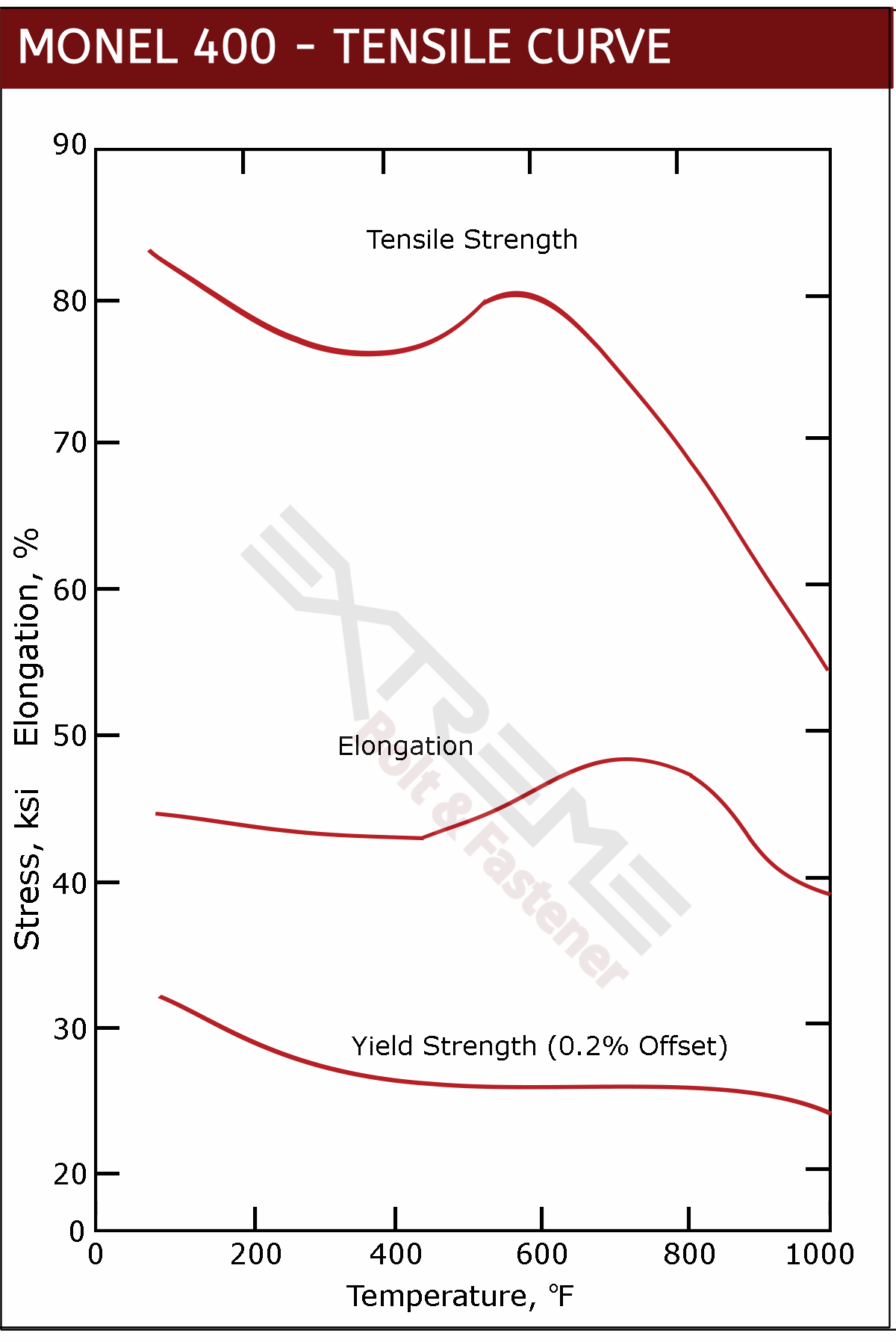
Strength and Toughness from Cryogenic to 1000°F
Monel socket head cap screws offer excellent mechanical properties over a wide temperature range from cryogenic up to 1000°F. In US Navy tear tests at temperatures as low as -320°F, Monel 400 has displayed excellent ductility and toughness. In fact, it has shown little decrease in impact resistance when tested on plates at liquid-hydrogen and liquid-helium temperatures.
Monel K500 is an age hardened alloy, known for extreme strength even at high temps. But it is also excellent for cryogenic service. Monel K500's tensile and yield strength increase - with little or no change to ductility and toughness - even at the temperature of liquid hydrogen.
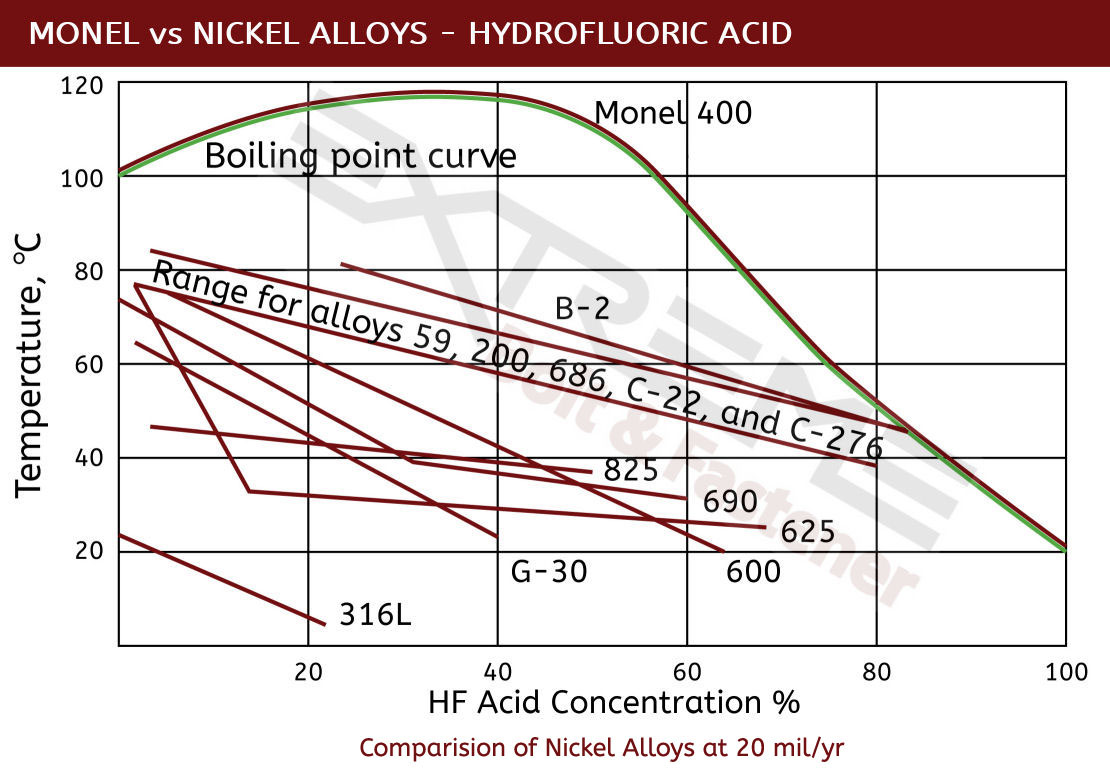
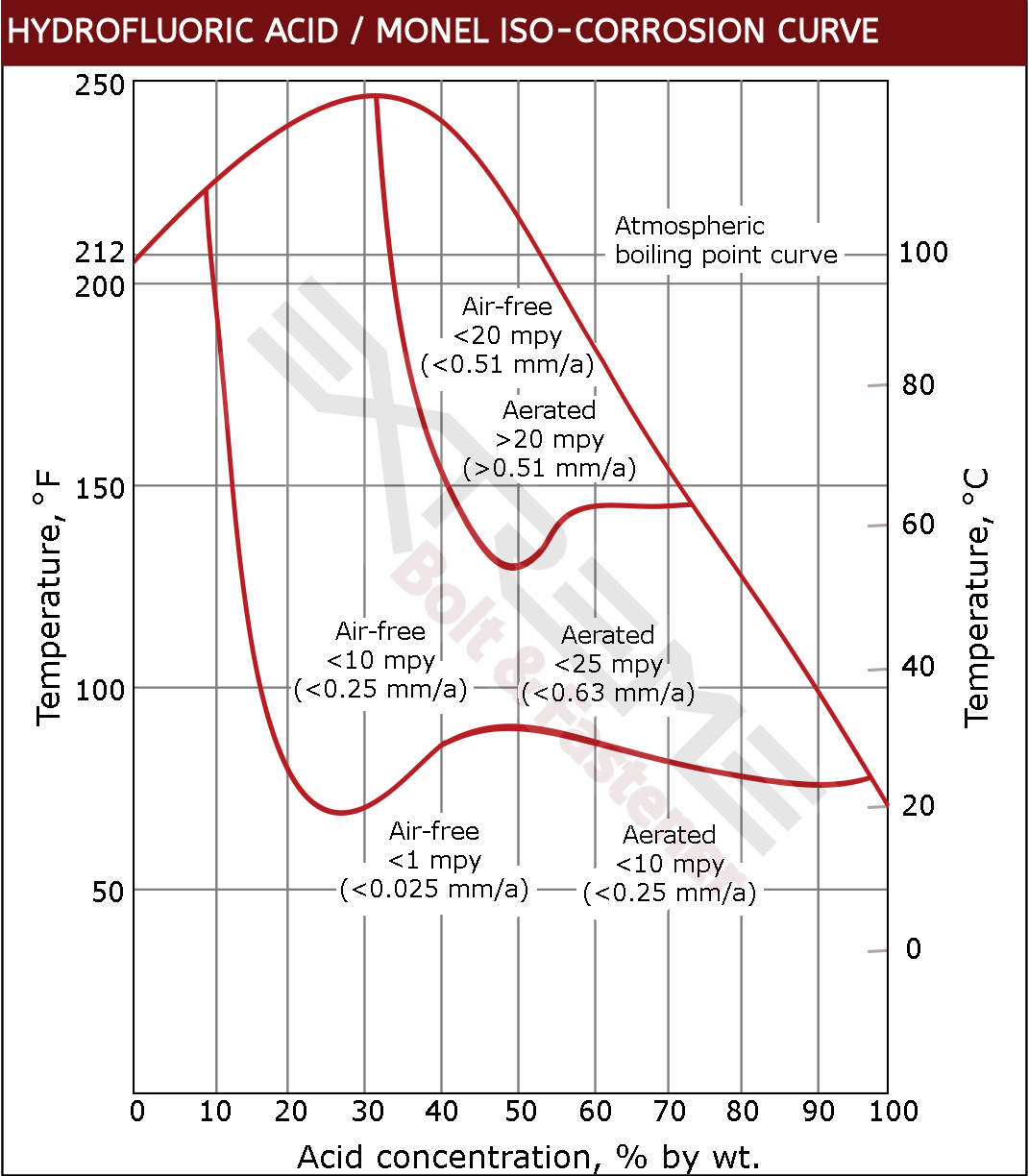
Excellent Resistance to Hydrofluoric Acid
One of the most outstanding characteristics of Monel socket head cap screws is that they offer exceptional resistance to hydrofluoric acid (HF), a particularly tough acid to deal with, in all concentrations up to the boiling point. For hydrofluoric acid applications Monel screws are perhaps the most resistant of all commonly used specialty alloys.
The most common grades of Monel flanges are Monel 400 and Monel K500 . Gain more insight on these two nickel alloy grades by accessing our Monel 400 and K500 overviews or by contacting our engineering experts.
Resources: Monel Torque Spec, Flange Dimensions, Flange Bolting Chart, Monel 400, Monel K500
Flange Types Available: Blind Flanges, Lap Joint Flanges, Slip On Flanges, Socket Weld Flanges, Threaded Flanges, Weld Neck Flanges
Common Grades of Lap Joint Flanges
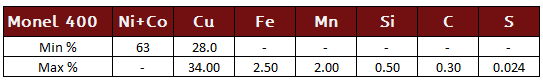
Monel 400
Monel 400, UNS N04400 (QQ-N-281), is a nickel-copper alloy with high strength and excellent corrosion resistance in a range of media including sea water, hydrofluoric acid, sulfuric acid, and alkalies. Monel 400 is commonly in marine engineering, chemical and hydrocarbon processing applications.
Monel 400 Specifications: BS3075NA13 (Wire), BS3076NA13 (Bar), ASTM B 164 (Rod, Bar, and Wire), ASTM B 564 (Forgings), ASME SB 164 (Rod, Bar, and Wire), ASME SB 564 (Forgings), AECMA PrEN 2305 (Wire for Rivets), SAE AMS 4675 (Bars and Forgings), SAE AMS 4730 (Wire), SAE AMS 4731 (Wire and Ribbon), DIN 17752 (Rod and Bar), DIN 17753 (Wire), DIN 17754 (Forgings), VdTÜV 263 (Sheet, Plate, Bar, and Tubing), QQ-N-281 (Plate, Sheet, Strip, Bar, Rod, Wire, and Forgings), Werkstoff 2.4360
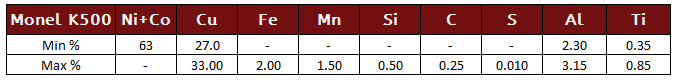
Monel K500
Monel K500, UNS N05500 (QQ-N-286), is a precipitation-hardenable nickel-copper alloy that combines the corrosion resistance of Monel alloy 400 with greater strength (over 2x as strong) and hardness. It also has low permeability and is nonmagnetic to temperatures as low as -150°F (-101°C).
Monel K500 Specifications: BS3075NA18 (Wire), BS3076NA18 (Rod and Bar), ASTM B 865 (Rod and Bar), DIN 17752 (Rod and Bar), DIN 17753 (Wire), DIN 17754 (Forgings), QQ-N-286 (Rod, Bar, Wire, and Forgings), SAE AMS 4676 (Rod and Bar), ASME Code Case 1192 (Rod and Bar), ISO 9723 (Bar), ISO 9724 (Wire), ISO 9725 (Forgings), Werkstoff 2.4375
Mechanical Properties of Monel
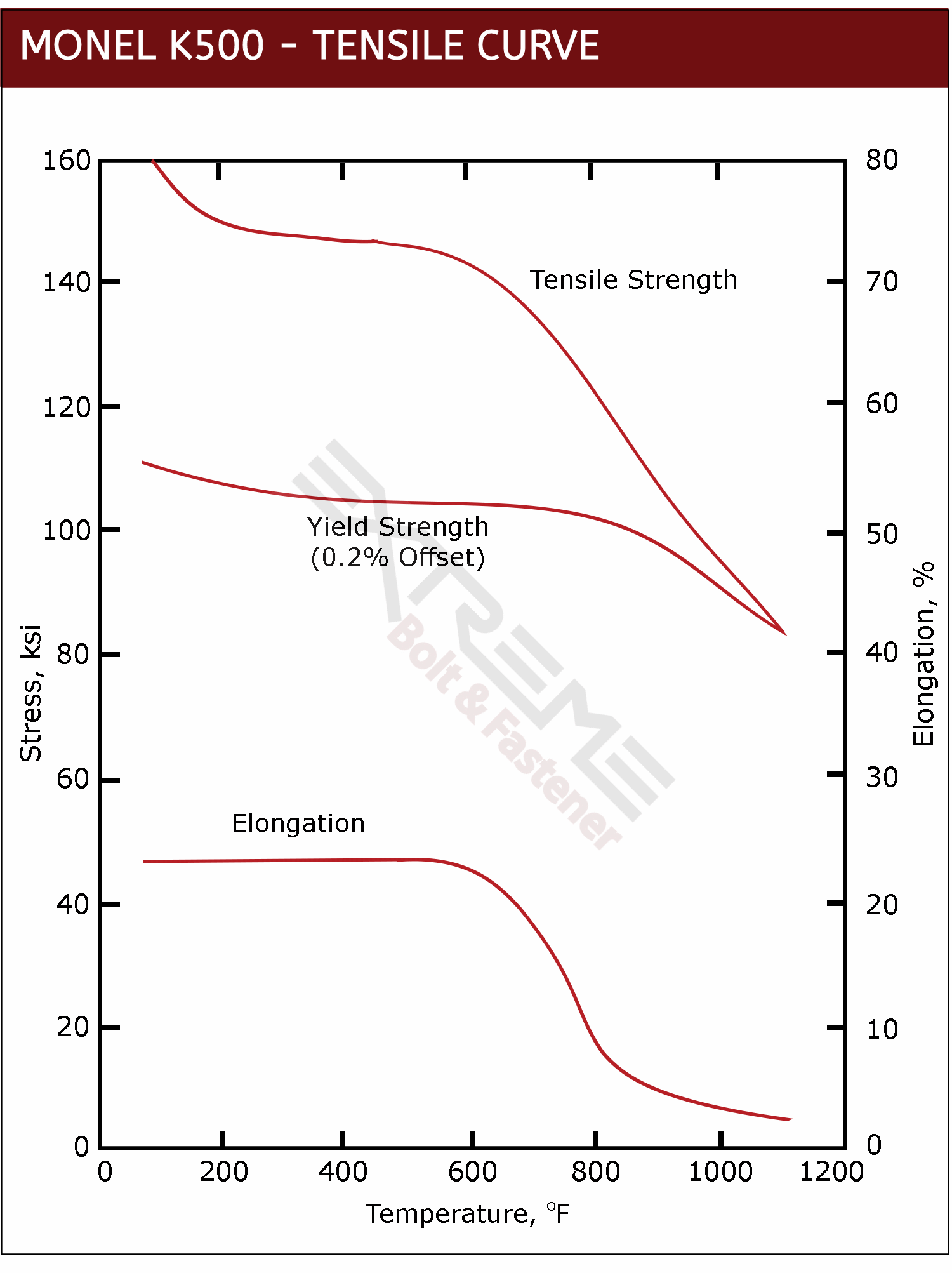
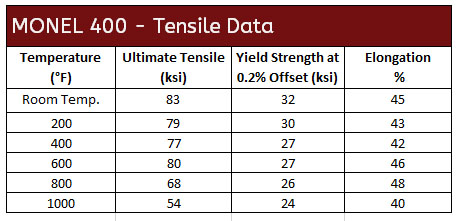
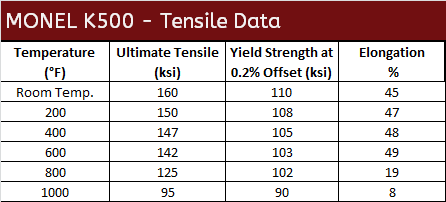
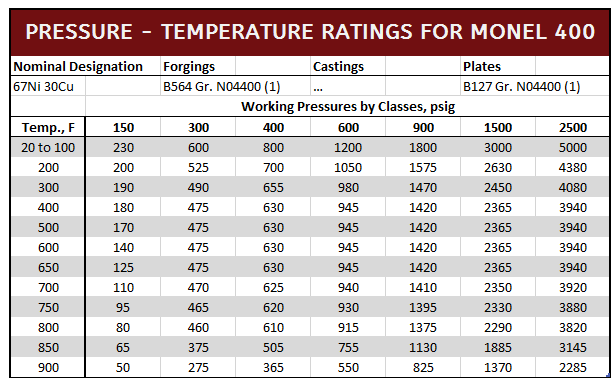
Monel 400 Corrosion Data
Monel Lap Joint Flange Features & Benefits
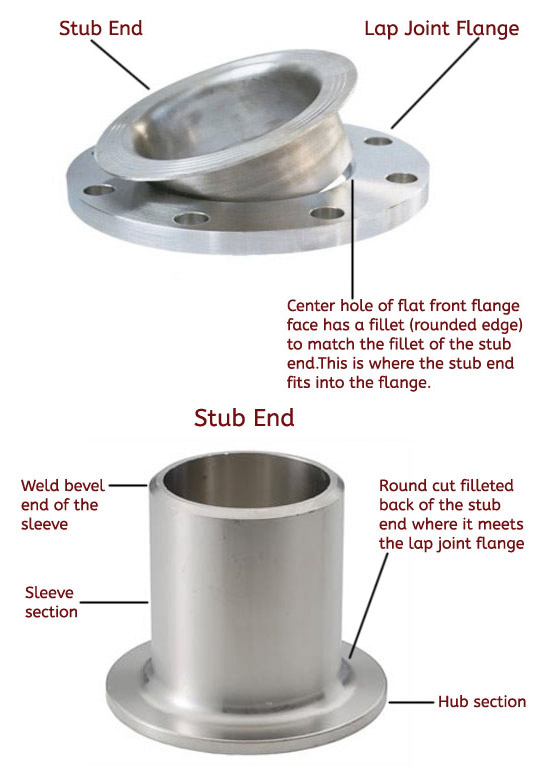
Lap joint flanges are unique in that they are made of two pieces, the flange itself and the stub end.
Flange
- The backside, has a slight shoulder that is square cut at the center or pipe hole
- The front side has a flat face with a filleted (rounded) center hole to match the filleted back face of the stub end. Here the stub end will wrap tightly around the center hole of the flange.
Stub End
- Shaped like a short piece of pipe with a weld bevel on one. This portion of the stub end is also called the sleeve.
- Narrow shoulder on the flange facing end called is the hub. The back face of the hub has a rounded transition (or inside fillet) that joins the hub to the sleeve
Benefits
- Economy
Because a lap joint flange has a two piece configuration, it offers a way to cut cost when piping systems requires - For high cost alloys the only "wetted" part is the stub end. In this situation, it is only required for the stub-end to be made of the higher cost corrosion-resistant material, where the flange itself can be the produced from lower cost steel.
- Ease of Work
By using lap joint flanges, work can be simplified in situations that require frequent and rapid disassemble and assembly during the operation of a plant. The ability to spin that backing flange compensates for misalignment of the bolt holes during assembly.


