When nickel, titanium or zirconium alloys are not enough...
- Immune to numerous acids and chemicals (corrosion tables)
- Better corrosion resistance than nickel alloys, titanium or zirconium
- High strength and stiffness in vacuum and inert gas up to 2000°C (3600°F)
- Can become brittle when used in oxygen above 300°C
- High purity and biocompatibilty
- Physical Properties
- Tantalum hex head cap screw features and benefits
- Tantalum grades, specifications and chemistry
- Datasheet for tantalum
Tantalum hex head cap screws are best known for its unmatched corrosion resistance and chemical inertness. Tantalum screws have a similar corrosion resistance to that of glass, but all of the typical mechanical and electrical properties of a metal.
Tantalum screws are also extremely stable at high temperatures, since tantalum has a melting point around 3000°C. High temperature applications require vaccum or inert gas since tantalum may embrittle when used in oxygen rich environments above 250°C. Tantalum hex head cap screws are also one of the most bio-compatible metals available and is also radio-opaque due to its high density (16.68 g/cm3).
All tantalum hex head cap screws are available in commercially pure tantalum and tantalum 2.5% tungsten (Ta-2.5%W).
Contact us to see if your required tantalum screws are in stock and how our engineers may help you with your tantalum fastener application.
Resources: Tantalum Torque Spec
Screw Types: Button Head Cap Screws, Flat Head Screws, Hex Cap Screws, Pan Head Screws, Set Screws, Socket Head Cap Screws, Tamper Resistant Security Screws,
Tantalum Hex Head Cap Screw Features and Benefits
It is important to differentiate between a tantalum hex head cap screw and hex head bolt. Often people assume they are the same, but they are actually very different fasteners in terms of how they are manufactured, as well as from an application perspective. Regardless of your choice, tantalum hex heads offer strong, stable joints because of their large head service.
The Hex Comparison
| Hex Head Cap Screw | Hex Head Bolts |
|
|
Tantalum Hex Head Cap Screw Advantages
The most important feature of a tantalum hex head cap screws is that it has a larger bearing surface area which provide better clamping pressure than other type of fastener such as a socket head cap screw. Additionally, since debris build up is less of an issue with this style of fastener verses a socket head cap screw, they are ideal of dirty applications where particles could clog up a socket. Though tantalum socket heads are typically used for tight access applications, hex heads can be a better choice when there is only side clearance available for tightening.
Tantalum Grades, Specifications and Chemistry
Tantalum (Commercially Pure)
Commercially pure tantalum metal is 99.95% pure tantalum has some o the best corrosion resistant properties of any metal. While its corrosion resistance is exceptional, it is relatively soft and mechanically similar in strength to copper.
Tantalum Specifications: UNS R05200, ASTM B521, ASTM B708, ASTM B365

Tantalum 2.5% Tungsten (Ta-2.5W)
This grade of tantalum alloyed with 2.5% tungsten provided better overall strength while maintaining its exception corrosion resistant properties. For tantalum fastener applications this is usually preferred.
Tantalum 2.5% Tungsten Specifications: UNS R05200, ASTM B521, ASTM B708, ASTM B365

Physical Properties
- Density 16.6 g/cc
- Melting Point 3290 K, 2996°C, 5462°F
- Boiling Point 5731 K, 6100°C, 9856°F
- Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (20°C) 6.5 x 10(-6) / °C
- Electrical Resistivity (20°C) 13.5 microhms-cm
- Electrical Conductivity 13% IACS
- Specific Heat .036 cal/g/°C
- Thermal Conductivity .13 cal/cm(2)/cm°C/sec
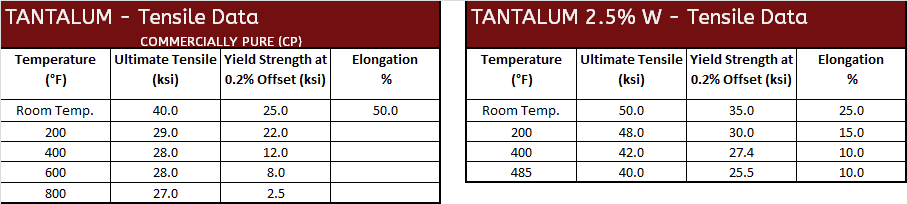
Tantalum Tensile Data
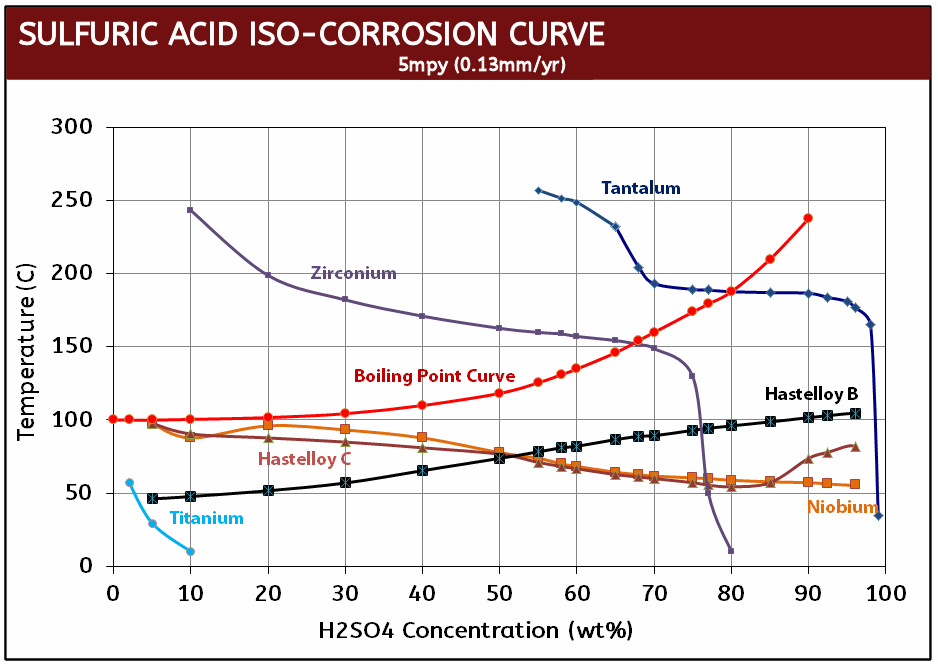
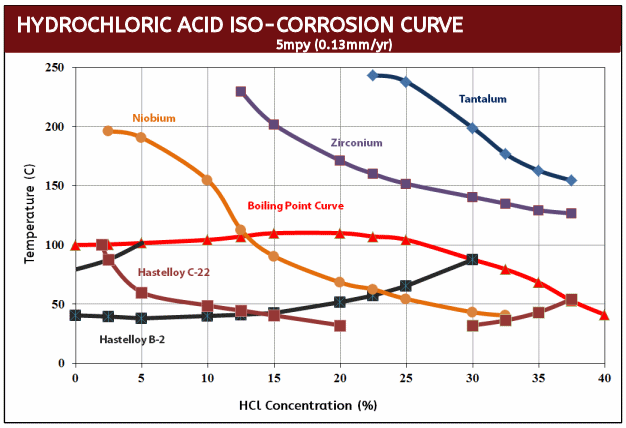
Tantalum Iso-Corrosion Curves
Tantalum Corrosion Resistance Table
TANTALUM SHOWS A NIL CORROSION RATE TO THE FOLLOWING MEDIAFor all temperatures up to at least 302F (150C) unless otherwise indicated | |||
Acetic acid | Chlorine, dry, <250°C (480°F) | Maleic acid | Potassium sulfate |
TANTALUM SHOWS LIMITED CORROSION RESISTANCE TO THE FOLLOWING MEDIA | |||
Air,>300°C (570°F) | Hydrogen, >300°C (570°F)Hydrogen fluoride | Potassium hydroxide, conc. | Sodium hydroxide, conc. |

